YF Risk List and WHO Map
WHO List: Countries with Risk of Yellow Fever Transmission
Certain countries require incoming travelers to show proof of yellow fever vaccination if they have been in countries with risk of yellow fever transmission. Unvaccinated travelers for whom immunization is legally required for entry may, upon arrival, be subject to surveillance and/or quarantine for up to 6 days if arriving within 6 days of departure from a yellow fever transmission risk country. Entry may be denied in some cases. Under the International Health Regulations, travelers may not be vaccinated at the port of entry against their will, but they may be quarantined in lieu of vaccination. A country is considered to have risk of yellow fever transmission if WHO reports that a potential risk of infection exists due to the presence of vectors (mosquitoes) and animal reservoirs (nonhuman primates harboring the yellow fever virus). Countries listed here appear in Annex 1: Countries with risk of yellow fever transmission as presented in WHO's International Travel and Health publication.
Countries with Risk of Yellow Fever Transmission
|
|
|
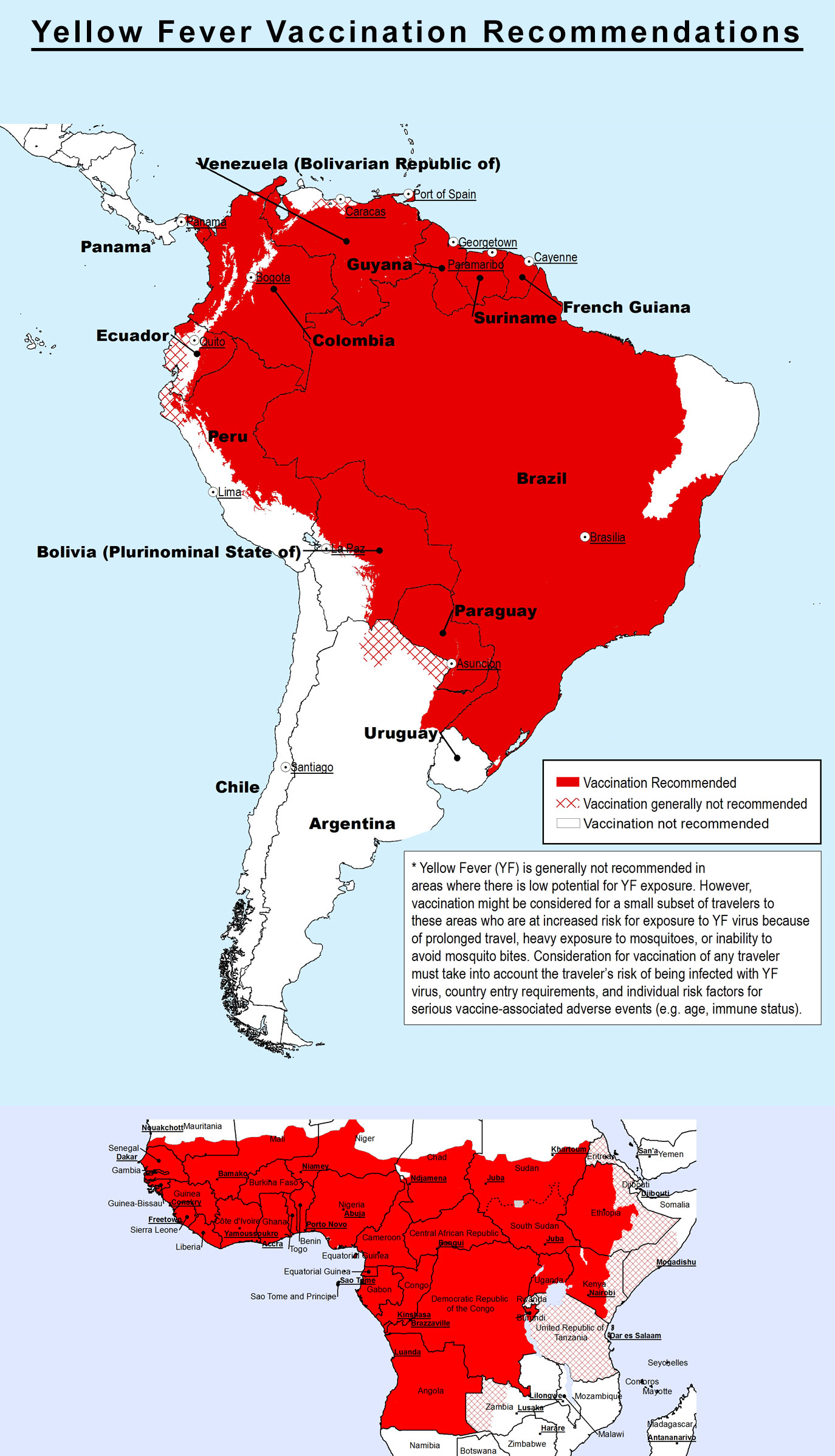
WHO Map: Yellow Fever Vaccination Recommendations
The following maps are taken from WHO's International Travel and Health publication. The shaded areas represent WHO's vaccination recommendations.